Information Technology Fundamentals
A study guide for CBSE Class 9 Computer Applications (Code 165). This guide covers Systems, Memory, Networking, and Multimedia.
1. The Computer System
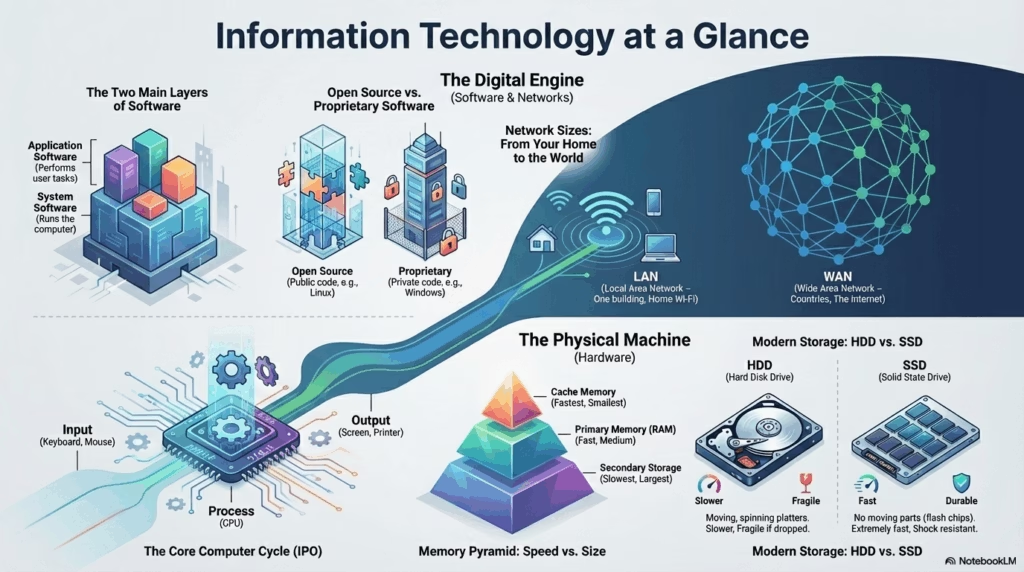
A computer is an electronic programmable device. It accepts data, processes it using algorithms, and produces information. It is not just one machine. It is a system of hardware and software working together.
Key Characteristics
- Speed: Executes millions of instructions per second (MIPS).
- Accuracy: Errors usually come from bad input. This is called GIGO (Garbage In Garbage Out).
- Diligence: No fatigue. It performs the millionth calculation as well as the first.
- Versatility: Can perform different tasks depending on the software.
How Computers Work: The IPO Cycle
Every computer follows a three-step process known as the Input-Process-Output cycle.
The CPU Engine
The Central Processing Unit has three main parts.
- ALU: Handles math and logic checks.
- CU: Directs traffic. It tells data where to go.
- Registers: High-speed temporary storage inside the CPU.
Evolution: Generations of Computers
| Gen | Core Technology | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Vacuum Tubes | Huge, generated heat, slow (ENIAC). |
| 2nd | Transistors | Smaller, faster, more reliable. |
| 3rd | Integrated Circuits (IC) | Keyboards/Monitors introduced. |
| 4th | Microprocessors (VLSI) | Current PCs. GUI OS introduced. |
| 5th | Artificial Intelligence | Voice recognition, Robotics, Learning. |
Types of Computers (By Size & Power)
The fastest and most expensive. Used for weather forecasting, nuclear research, and space exploration.
Example: PARAM, Summit.
Handles huge amounts of data for large organizations (Banks, Airlines). Supports hundreds of users simultaneously.
Mid-size. More powerful than a PC but less than a mainframe. Used as small servers.
Small, inexpensive, designed for individual use.
Example: Desktop, Laptop, Smartphone, Tablet.
2. Memory and Storage
Memory follows a hierarchy based on speed and cost. The CPU needs data fast, but fast memory is expensive. We use a mix of Primary and Secondary memory.
Visualizing Memory Hierarchy
The top of the pyramid is fastest but smallest. The bottom is slowest but largest.
Memory Measurement Units
| Bit (b) | Binary Digit (0 or 1). The smallest unit. |
| Nibble | Group of 4 bits. |
| Byte (B) | Group of 8 bits. Represents one character. |
| Kilobyte (KB) | 1024 Bytes (210). |
| Megabyte (MB) | 1024 KB. |
| Gigabyte (GB) | 1024 MB. Standard for RAM sizes. |
| Terabyte (TB) | 1024 GB. Standard for Hard Disk sizes. |
Primary Memory
| Feature | RAM (Random Access Memory) | ROM (Read Only Memory) |
|---|---|---|
| Types | SRAM, DRAM | PROM, EPROM, EEPROM |
RAM Variants
- SRAM (Static): Faster, expensive, used for Cache. Does not need refreshing.
- DRAM (Dynamic): Slower, cheaper, used for Main Memory. Needs constant refreshing.
ROM Variants
- PROM: Programmable once by user.
- EPROM: Erasable via UV light.
- EEPROM: Erasable electronically (Flash memory).
Secondary Storage Explorer
Click the buttons below to filter specific storage technologies.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
MagneticUses spinning platters. High capacity (Terabytes) but mechanical parts make it slower.
CD-ROM
OpticalCapacity: 700MB. Uses Red Laser (780nm). Good for small files.
DVD
OpticalCapacity: 4.7GB. Uses Red Laser (650nm). Standard for video.
Blu-ray
OpticalCapacity: 25GB-50GB. Uses Blue-Violet Laser (405nm). High Definition content.
Pen Drive
Solid StateUses EEPROM. No moving parts. Connects via USB. Highly durable.
Sony Memory Stick
Solid StateProprietary format by Sony (1998). Used “MagicGate” encryption for DRM protection.
Modern Storage Battle: HDD vs SSD
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Parts | Moving parts (Spinning platters) | No moving parts (Flash chips) |
| Speed | Slower read/write | Extremely fast |
| Durability | Fragile if dropped | Shock resistant |
3. Input and Output
Essential Input Devices
Keyboard
Text input. QWERTY layout is standard.
Mouse
Pointing device. Controls cursor movement.
Web Cam
Captures video for calls. Input is visual data.
Scanner
Digitizes physical photos/docs into images.
Output: Visual Display Units (Monitors)
CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) ▼
LCD / LED (Liquid Crystal / Light Emitting Diode) ▼
Specialized Input Technologies
Used for checking objective test answer sheets (bubbling).
Scans vertical lines to identify products in shops.
Used in banks to process cheques quickly.
The Plotter (Special Output)
Unlike regular printers, plotters use pens to draw continuous lines. They are used by engineers and architects for high-quality blueprints, maps, and construction plans (CAD).
Printer Technologies: Impact vs. Non-Impact
Printers are classified by how they put ink on paper. Impact printers strike the paper physically. Non-impact printers do not.
| Feature | Impact (e.g., Dot Matrix) | Non-Impact (e.g., Laser, Inkjet) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Hammer strikes ribbon | Sprays ink or fuses toner |
| Noise | High (Noisy) | Low (Quiet/Silent) |
| Unique Ability | Can make Carbon Copies | High resolution photos |
Connecting Hardware: Ports & Cables
🔌 USB (Universal Serial Bus)
The standard for connecting peripherals like mice, keyboards, and printers. It provides both data transfer and power.
📺 HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
Transmits high-quality video and audio over a single cable. Standard for monitors and projectors.
🎧 Audio Ports (3.5mm Jack)
Green port for Output (Speakers/Headphones). Pink port for Input (Microphone).
🌐 Ethernet (RJ45)
Used for wired network connections. Looks like a large telephone jack.
4. Software Architecture
System Software
The base layer. Includes the Operating System (OS) which manages resources, and Device Drivers that let the OS talk to hardware.
- • Process Management: CPU scheduling.
- • Memory Management: Allocating RAM.
- • File Management: Organizing data on disk.
- • Device Management: Controlling I/O.
Interacting with the OS: Interfaces
CUI / CLI
Character User Interface
User types text commands to perform tasks. Requires memorizing commands. No mouse use.
C:\> COPY file.txt
Examples: MS-DOS, Unix.
GUI
Graphical User Interface
User interacts with visual elements like Icons, Menus, and Windows using a Mouse or Touch.
Examples: Windows, macOS, Ubuntu.
Application Software
Software designed for end-users to perform specific tasks.
Utility Software
Housekeeping tools that maintain the computer’s health.
- Antivirus: Protects against malware.
- Backup Software: Creates copies of data.
- Compression: Reduces file size (WinZip).
- Disk Defragmenter: Reorganizes files for speed.
Language Processors
Translators that convert High-Level Code into Machine Code (0s and 1s).
- Assembler: Converts Assembly Language.
- Compiler: Translates whole program at once (Fast execution).
- Interpreter: Translates line by line (Easier debugging).
Mobile Applications
Apps on phones run differently than PC software. The APU (Application Processing Unit) handles these on mobile devices.
- Native Apps: Built for specific OS (iOS/Android). Fastest.
- Web Apps: Websites that look like apps. Run in browser.
- Hybrid Apps: Web apps wrapped in a native container.
Software Licensing Types
Open Source Software (OSS)
The source code is available to the public. Users can modify, study, and distribute it.
Proprietary Software
Owned by a company. Source code is hidden. Users must buy a license to use it.
5. Computer Networking
Network Types (By Size)
- PAN (Personal Area) Smallest range. Bluetooth connects phone to headset.
- LAN (Local Area) Single building or room. High speed. Wi-Fi in a house.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area) Covers a city. Example: Cable TV network or City-wide Wi-Fi.
- WAN (Wide Area) Spans countries. The Internet is the biggest WAN.
Communication Media
🔌 Wired (Guided)
Signals travel through physical cables.
- Twisted Pair: Common Ethernet cables (RJ45).
- Fiber Optic: Uses light. Fastest. Expensive.
- Coaxial: Cable TV wire.
📡 Wireless (Unguided)
Signals travel through air/space.
Network Topologies
Topology refers to the physical layout of the network.
Network Hardware Devices
Converts digital computer signals into analog signals (for telephone lines) and back again.
Intelligent device. Connects devices in a LAN. Sends data only to the specific device that requested it (unlike a Hub).
Connects different networks together (e.g., your Home LAN to the Internet WAN). Routes data packets via IP addresses.
Key Internet Terminology
A company that provides access to the internet.
Examples: Airtel, Jio, Verizon.The unique address of a webpage.
Example: https://www.rezyo.inA unique numerical label assigned to every device connected to a network.
Example: 192.168.1.1A system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet.
Cloud Computing
Using internet servers to store data instead of a local hard drive.
6. Multimedia
Multimedia combines text, audio, graphics, video, and animation. Interactivity is key.
Common File Formats
| Type | Extensions | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Image | .JPG, .PNG, .GIF | Photos, Transparent graphics, Animations. |
| Audio | .MP3, .WAV | Music tracks, Sound effects. |
| Video | .MP4, .MKV, .AVI | Movies, YouTube clips. |
Knowledge Check
Because it processes all instructions, performs calculations (ALU), and controls the flow of data (CU), much like a human brain controls the body.
Hint: Think about where decisions happen.
Volatility. RAM is volatile (loses data without power), while ROM is non-volatile (retains data without power). RAM is for working; ROM is for booting.
CD (700MB) < DVD (4.7GB) < Blu-ray (25GB) < Hard Disk (TB).
MagicGate. It was a copyright protection technology to encrypt data.