Unit 2: Cyber-Safety and Digital Hygiene
Updated Nov 2025 | CBSE Class IX (Code 165) | 20 Min Read
Core Topics Overview
Safe Browsing, Encryption (Caesar Cipher), IT Act 2000, Emerging Threats (Deepfakes), Identity Protection, Digital Wellness.
Architecture of Safe Web Browsing
Browsing initiates complex data exchanges. The browser sends requests to servers containing metadata. This metadata identifies the user and their behavior.
Tracking Mechanics
- IP Addressing: Numerical labels assigned to devices. They reveal geographical location and ISP.
- Cookies: Text files storing state. Third-party cookies track users across different domains for profiling.
- Fingerprinting: Scripts query device configurations (screen size, fonts) to create a unique ID without cookies.
Defense Tools
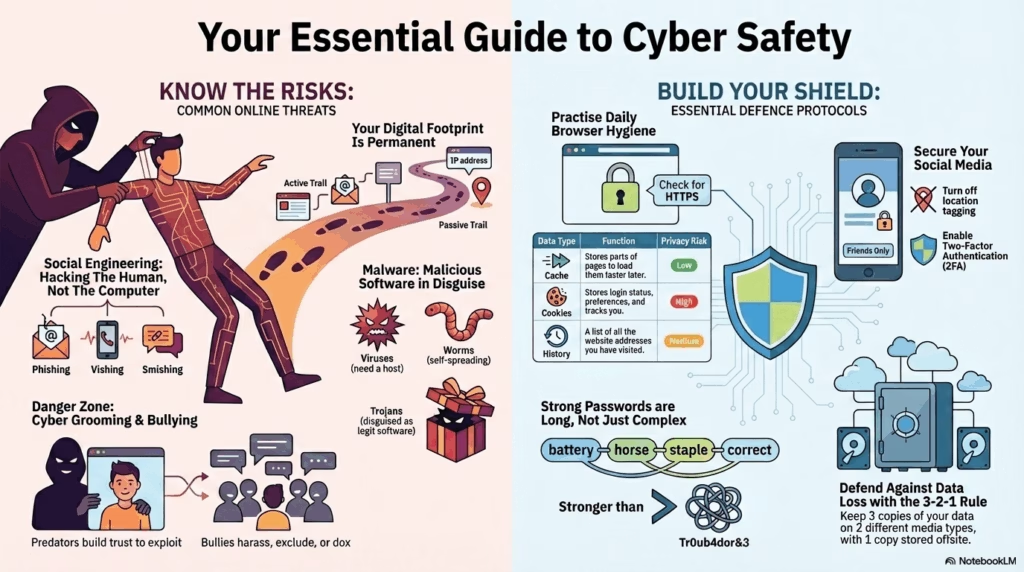
- HTTPS: Encrypts data transfer. The padlock icon indicates encryption and server authentication.
- Incognito Mode: Prevents local history storage. Does not hide activity from ISPs or websites.
- VPN: Creates an encrypted tunnel. Masks IP address from external observers.
Visualizer: HTTP vs HTTPS Data Path
Red dots represent unencrypted data packets. Green dots represent encrypted packets.
Encryption Mechanics: The Caesar Cipher
Modern encryption (like AES used in HTTPS) is complex, but it started with simple substitution. The Caesar Cipher shifts every letter by a fixed number.
*Try typing your name. Notice how if the key (shift) is known, the message is easily broken. Modern encryption uses keys with trillions of possibilities.
Public Wi-Fi Protocols
Open networks (cafes, airports) are susceptible to Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks where hackers intercept data between you and the router.
Avoid
Banking transactions, entering passwords, or shopping on public Wi-Fi.
Adopt
Use a VPN or mobile data (hotspot) for sensitive tasks. Turn off “Auto-Connect” features.
Daily Browser Hygiene Checklist
Clear Cache & Cookies: Regularly purge temporary files to remove tracking scripts and free up space.
Update Browser: Ensure automatic updates are ON. Outdated browsers have unpatched security holes.
Check Extensions: Audit installed extensions. Remove any that you don’t recognize or don’t use.
Pop-up Blocker: Keep this enabled to prevent malicious ads (Adware) from opening automatically.
Online Gaming Protocols
Multiplayer environments are prime targets for social engineering and cyberbullying.
Players who deliberately irritate or harass others to ruin the game experience. Action: Mute and Report immediately.
Phishing sites promising “Free Skins” or “V-Bucks”. Action: Never enter login details on third-party generator sites.
Predators use voice chat to build trust with minors. Action: Use voice changers or restrict chat to “Friends Only”.
How Search Engines Work
Search engines don’t search the *live* web in real-time. They search their own index.
Automated bots (“Spiders”) browse the web, following links from page to page.
Organizing the content found during crawling into a massive database (The Index).
Algorithms determine the most relevant results for your query (e.g., PageRank).
Browser Data: What are you deleting?
| Data Type | Function | Privacy Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Cache | Stores images/scripts to load pages faster on next visit. | Low (Mostly performance data). |
| Cookies | Stores login status, preferences, and cart items. | High (Used for tracking/profiling). |
| History | List of URLs visited. | Medium (Reveals habits if device is shared). |
Social Network Protocol
Social platforms require specific hygiene practices to prevent data leakage and identity cloning.
Profile Locking
Restrict visibility of posts and photos to “Friends Only”. Public profiles are easily scraped by bots for identity theft.
Geolocation Tags
Disable auto-tagging of location in photos. Real-time location sharing facilitates physical stalking.
Friend Acceptance
Verify identities offline before accepting. Fake accounts often use stolen photos to infiltrate friend networks.
2FA (Two-Factor Auth)
Enable SMS or App-based authentication. Even if a password is stolen, the account remains secure without the second code.
💳 Secure Payment Hygiene
CVV Secrecy: Never share the 3-digit code on the back of your card via phone/email.
OTP Alert: Bank employees will NEVER ask for your OTP. It is for your eyes only.
Virtual Keyboards: Use on-screen keyboards for banking to defeat Keyloggers.
Email Forensics: “From” vs “Reply-To”
Hackers can spoof the “From” name to look like your Principal or Boss. Always check the actual email header.
From: “Principal Desk” <admin@school.com> // Looks Legit
Reply-To: hacker123@freemail.com // The Trap!
Subject: Urgent Fee Payment
…Click here to pay…
Always hover over the sender name to reveal the actual email address.
Mobile App Safety: Permission Audits
Apps often ask for more data than they need. Always question the relevance of the permission.
Digital Shredding: Why “Delete” isn’t enough
When you delete a file or format a drive, the data is not erased. The operating system simply marks the space as “available”. Specialized software can recover this data.
Standard Delete
Like removing the table of contents. The book pages (data) remain.
Secure Wipe (Shredding)
Overwrites the actual data with random 0s and 1s multiple times. Impossible to recover.
Identity Protection & Ethics
⚠ Danger Zone: Cyber Grooming
A predatory process where an adult builds an emotional bond with a child online to gain their trust for sexual abuse or exploitation.
The Tactics
- Secrecy: “Don’t tell your parents, they won’t understand us.”
- Gifts: Offering game skins, recharge packs, or money.
- Flattery: Excessive compliments to boost ego.
The Defense
- Zero Secrecy: Never keep online friends a secret from guardians.
- Refuse Gifts: Nothing online is truly “free”.
- Block & Report: Immediate disengagement.
Digital Footprint Analysis
Your digital footprint is permanent. It is categorized into two types:
👣 Active Footprint
Data you knowingly submit or publish.
- Posting photos on Instagram/Snapchat.
- Sending emails or WhatsApp messages.
- Filling out online surveys.
🕵️ Passive Footprint
Data collected without your explicit action.
- IP Address logging by websites.
- Search history tracking by Google/Bing.
- Device GPS location history.
| Concept | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Privacy | Right of the individual to control personal data. | Setting an Instagram profile to “Private”. |
| Confidentiality | Duty of the receiver to protect trusted data. | School keeping grades secure. |
| Digital Footprint | Trail of data left by online activities. | Comments, likes, IP logs. |
Social Engineering: Hacking the Human
Attacks that manipulate people into revealing confidential information rather than hacking software directly.
🚩 How to Spot a Fake Link
Phishing
Fraudulent emails mimicking trusted sources (e.g., “Bank Update Required”) to steal credentials.
Vishing
“Voice Phishing”. Fraudulent phone calls posing as support staff asking for OTPs.
Smishing
Phishing via SMS text messages containing malicious links.
Cyber Stalking Explained
Cyber stalking involves the use of the internet to harass, intimidate, or cause fear to a specific individual. It differs from general spam due to its targeted and persistent nature.
Primary Indicators:
Forms of Cyber Bullying
- Flaming: Online fights using electronic messages with angry and vulgar language.
- Exclusion: Intentionally leaving someone out of a group chat or online game to hurt them.
- Masquerading: Creating a fake identity to harass someone anonymously.
- Doxing: Publicly revealing private personal information (address, phone number) about an individual.
Key Sections of the IT Act, 2000
The Information Technology Act is the primary law in India dealing with cybercrime and electronic commerce.
Section 66C
Identity TheftPunishment for fraudulently making use of the electronic signature, password or any other unique identification feature of any other person.
Section 66D
PersonationPunishment for cheating by personation (pretending to be someone else) using computer resources or communication devices.
Section 67
ObscenityPunishment for publishing or transmitting obscene material in electronic form.
Section 43
DamagesDeals with civil liability (compensation) for damage to computers (viruses, denial of service, data theft) without permission.
Netiquette (Digital Etiquette) Basics
- No Spamming: Avoid sending repeated, irrelevant messages.
- Respect Copyright: Do not plagiarize content; give credit.
- No Trolling: Avoid deliberately provoking others for reaction.
- Empathy: Remember there is a human behind the screen.
Digital Ethics: Intellectual Property
Software Licensing Models
Freeware
Copyrighted software available at no cost for unlimited use, but source code is hidden (e.g., Skype, Chrome).
Shareware
Software provided free on a “trial basis”. Payment is required for continued use or full features (e.g., WinRAR).
FOSS / OSS
Free and Open Source Software. Users can view, modify, and redistribute the source code (e.g., Linux, Firefox, LibreOffice).
Understanding Creative Commons (CC) Symbols
CC BY (Attribution)
Must credit the author.
CC NC (Non-Commercial)
Personal use only. No profit.
CC ND (No Derivs)
Cannot edit/remix work.
CC SA (Share Alike)
Must license new work same way.
Digital Wellness & Ergonomics
Safety isn’t just about data; it’s about physical health.
Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds to prevent eye strain.
Hold devices at eye level. Looking down for long periods strains the cervical spine.
E-Waste: The Environmental Footprint
Electronic waste contains toxic materials like Lead and Mercury. Never throw old phones/batteries in the dustbin.
Action: Locate your nearest authorized “E-Waste Collection Center”.Authentication Security
Password strength relies on entropy (randomness). Length often beats complexity.
Tr0ub4dor&3
Predictable substitutions.
battery horse staple correct
Long, random phrases.
Malware Analysis
Emerging Threats 2.0
AI & QR BasedDeepfakes
Media (Video/Audio) generated by AI that convincingly replaces a person’s likeness or voice with another’s.
How to Spot:
- Unnatural blinking patterns (too much or too little).
- Lip-sync issues (audio doesn’t perfectly match mouth).
- Inconsistent lighting or shadows on the face.
Quishing
“QR Code Phishing”. Attackers paste fake QR stickers over real ones (e.g., at parking meters) or send QRs via email to bypass filters.
Defense Protocol:
- Inspect physical stickers for tampering/overlay.
- Preview the URL before the site loads (most scanners allow this).
- Never pay via a QR code sent in an unsolicited email.
DDoS Attack (Distributed Denial of Service)
An attack meant to crash a website by flooding it with traffic.
The “Traffic Jam” Analogy
Imagine 1,000 fake cars suddenly blocking a highway. The real cars (legitimate users) cannot get through to their destination (website).
The Pillars of Cyber Security: The CIA Triad
Confidentiality
Preventing unauthorized access (Encryption, Passwords).
Integrity
Ensuring data is not altered/tampered with (Checksums).
Availability
Ensuring data is accessible when needed (Backups, preventing DDoS).
The Digital Gatekeeper: Firewall
A Firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules.
Analogy
Like a security guard at a gated community. They check the ID of every visitor (data packet) against a list of allowed guests (rules).
Firewall vs Antivirus
- Firewall: Filters traffic before it enters the network. (Prevention)
- Antivirus: Scans files after they enter the system. (Detection/Cure)
Virus
Needs a host file. Requires user execution to replicate. Destructive payload. Often attached to .exe or .doc files.
Worm
Standalone program. Self-replicating via networks. Does not need user action. Consumes bandwidth.
Adware
Advertising software. Automatically renders ads to generate revenue. Often bundles Spyware to track habits.
Botnets (Zombie Army)
A network of infected computers controlled remotely by a hacker without the owners’ knowledge. These “zombies” are used to launch massive attacks (DDoS) or send spam.
Ransomware
Malware that encrypts user data, demanding payment (ransom) for the decryption key. Backup is the only robust defense.
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule:
- Keep 3 copies of your data.
- Store them on 2 different media types (e.g., Hard Drive + Cloud).
- Keep 1 copy offsite (different physical location).
Trojan Horse
Malware disguised as legitimate software (e.g., a free game) to trick users into installing it. It creates “backdoors” for hackers.
How Antivirus Software Works
Signature Detection
Compares files against a massive database of known virus “signatures” (code snippets). Effective against known threats.
Heuristic Analysis
Scans for suspicious *behavior* (e.g., a file trying to delete system folders) rather than specific code. Effective against new, unknown threats (Zero-day).
System Diagnostics: Is your device infected?
- Performance Lag: Significant slowdown in processing speed or boot time.
- Pop-up Storms: Frequent ad windows appearing even when the browser is closed (Adware sign).
- Browser Redirection: Search queries redirect to unknown or malicious search engines.
- Disabled Security: Antivirus or Firewall turns off automatically and cannot be restarted.
Reporting Mechanisms (India)
Step 1: Evidence Collection
Take screenshots of chats, profiles, and URLs. Do not delete the content immediately.
Step 2: Platform Reporting
Use the “Report User” or “Report Post” button on the specific social media app.
Step 3: Legal Escalation
Visit cybercrime.gov.in (NCRP) or dial 1930 for financial fraud.
cybercrime.gov.in: Central portal for reporting all cybercrimes. Allows anonymous reporting for specific offenses.
Helpline 1930: Immediate reporting for financial fraud. Integrated with banks to freeze fraudulent fund transfers.